Page 4 - Dyslipidaemia_newsletter8_2024_Final
P. 4
REFLECTIONS
Dyslipidaemia
Dyslipidaemia Global Newsletter #8 2024
Inflammation, cholesterol, lipoprotein(a), and 30-year cardiovascular outcomes in Dyslipidaemia
women.
Ridker PM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2024 Aug 31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2405182. Online ahead of print.
The Women’s Health Study (WHS) was a prospective study of 39,876 initially healthy women who were followed over a period of
30 years to assess three biomarkers, LDL-C, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), and lipoprotein(a), and the occurrence of
cardiovascular events, specifically a composite endpoint of incident myocardial infarction, coronary revascularisation procedures,
stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes.
While the measurement and reduction of LDL-C is a cornerstone of dyslipidaemia management, high-sensitivity CRP, a biomarker of
low-grade vascular inflammation, and lipoprotein(a), a genetically determined lipid fraction, have also become important for targeting
cardiovascular interventions.
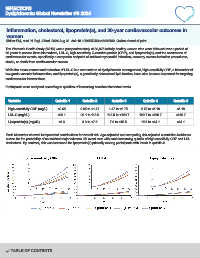
Participants were analyzed according to quintiles of increasing baseline biomarker levels.
Variable Quintile 1 Quintile 2 Quintile 3 Quintile 4 Quintile 5
High-sensitivity CRP (mg/L) <0.65 0.65 to <1.47 1.47 to <2.75 2.75 to <5.18 ≥5.18
LDL-C (mg/dL) <96.1 96.1 to 113.5 113.5 to <129.7 129.7 to <150.7 ≥150.7
Lipoprotein(a) (mg/dL) <3.6 3.6 to <7.6 7.6 to <15.5 15.5 to <44.1 ≥44.1
Each biomarker showed independent contributions for overall risk. Age-adjusted and competing risk-adjusted cumulative incidence
curves for the probability of an incident major adverse CV event rose with each increasing quintile of high-sensitivity CRP and LDL
cholesterol. By contrast, risk was increased for lipoprotein(a) primarily among participants with levels in quintile 5.
TABLE OF CONTENTS